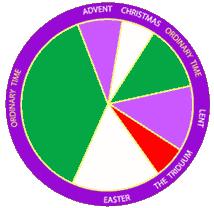
The Easter Season officially concluded on the Feast of Pentecost two weeks ago, and and on the following Monday we began “Ordinary Time” anew with the colors of the vestments and altar furnishings returning to green from the violet of Lent and the white of Easter. What’s so “ordinary” about it? Actually, “Ordinary Time” is the English translation of the Latin Tempus Per Annum (“time throughout the year”) and gets its name from the word ordinal, meaning “numbered,” because we begin to count the weeks rather than the seasons. Ordinary Time, depending on the year, runs either 33 or 34 weeks, and makes up the time in the Church calendar that does not fall within the seasons of Advent, Christmas, Lent, or Easter.
The Church celebrates two periods as Ordinary Time. The first period, ran from the end of Christmas until the evening of Mardi Gras when Lent begins, followed by Easter. The second period begins on the Monday after Pentecost and runs until Advent begins again in November. This period includes Christ the King Sunday, the final Sunday of Ordinary Time.
The use of the term “Ordinary Time” was used before the Second Vatican Council, but it was not until after the council that the term was officially used to designate the period between Epiphany and Lent, and the period between Pentecost and Advent. The older names for those seasons were the “Season After Epiphany” and the “Season After Pentecost.”
Ordinary Time celebrates the mystery of the life of Christ in all its aspects, and contains many important liturgical celebrations, including, Trinity Sunday, Corpus Christi, the Assumption of Mary, he Exaltation of the Holy Cross, All Saints, All Souls and Christ the King. In addition, the Church continues to celebrate other feast days of Mary, feasts of many saints, and the Solemnity of Sts. Peter and Paul.